In order to become the leading gastroenterology practice in the Northeast region, it’s not enough to simply be the largest or the most experienced – you also must be the most advanced. At US Digestive Health, that’s at core of everything we do.

A PATIENT-CENTERED APPROACH
Providing Specialized Care Through a Patient-Centered Approach
Our practice is built entirely around you, the patient, to provide more specialized care, better outcomes, and greater satisfaction. As the most experienced GI team in the region, we combine our extensive medical expertise with technological advancements and research breakthroughs to deliver new answers and options for every patient we treat.
Technology & innovation
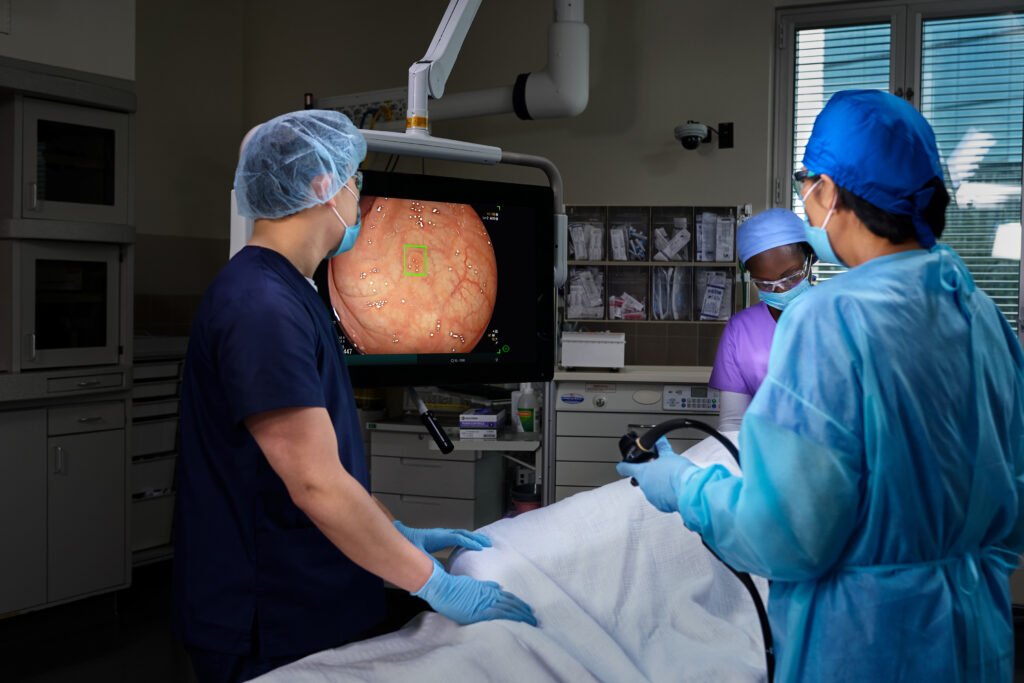
Doing More to Save Lives with The Platinum Standard® in Colonoscopy.
We are on a mission to eliminate the nation’s 2nd most deadly cancer, which is why we’ve invested in the latest, most powerful AI-enabled screening technology — to elevate detection rate accuracy and save more lives.

Locations
Opening Access to Cutting-Edge Research and Advanced Digestive Care.
As the leading gastroenterology provider in the Northeast, we bring the best in digestive care to our communities. Our team of over 250 providers treat the entire spectrum of digestive health conditions and have expanded to 37 offices, 23 ASCs, and 4 clinical research sites, making us one of the largest digestive care providers in the nation.
skip the office trip
Fast-Track Your Colonoscopy
For adults 45 and older, scheduling a colonoscopy is now easier than ever. Using our new Fast Track Program, patients can now get pre-approved and “skip the line” for their colonoscopy without a trip into one of our regional offices.


Newsroom
10 signs you could be anemic
If you suspect that you might be anemic, you might wonder what symptoms and signs to look for. Because anemia involves your blood, it can affect many different aspects of your health.










